The Hercules beetle is a true marvel of nature, often regarded as the strongest insect on Earth. With its incredible strength, fascinating appearance, and vital role in ecosystems, the Hercules beetle captivates both scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Found primarily in the tropical regions of Central and South America, this impressive beetle species showcases natural power in a way that few others can match. The Hercules beetle is not only known for its physical strength but also for its remarkable size, behavior, and ecological significance. In this article, we will explore the key features of the Hercules beetle, its impressive strength, lifecycle, habitat, and the unique role it plays in maintaining the health of the environment. By understanding these aspects, we can better appreciate why this insect holds such a prestigious position in the animal kingdom.
Introduction to the Hercules Beetle
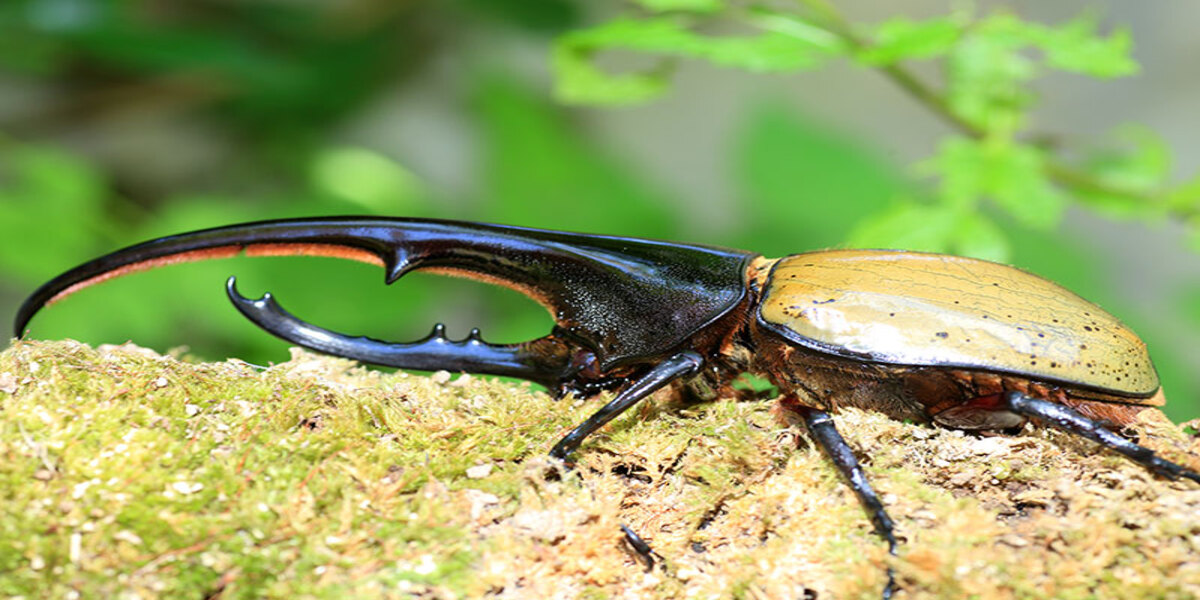
The Hercules beetle (Dynastes hercules) is one of the largest and most powerful beetles in the world, belonging to the family Scarabaeidae. Named after the Greek mythological hero Hercules, who was known for his incredible strength, this beetle is an apt representative of nature’s raw power. Its sheer size and strength make it stand out among other beetles. Adult Hercules beetles can reach up to 7 inches in length, making them among the largest insects in the world. Despite their intimidating appearance, these beetles are harmless to humans and play an important role in the environment as decomposers.
Native to the rainforests of Central and South America, particularly in countries like Costa Rica, Panama, and Colombia, Hercules beetles are most commonly found in tropical habitats with abundant vegetation. These areas provide the perfect conditions for the beetles to thrive, with the moist environment and access to decaying plant material that forms a primary part of their diet. Hercules beetles are nocturnal, which means they are most active at night when they forage for food and mate.
Physical Characteristics of the Hercules Beetle
The Hercules beetle is easily recognizable by its striking physical features. One of its most prominent characteristics is its large, curved horns. The male Hercules beetle possesses a pair of large, backward-curved horns on its head, which it uses during combat with other males for dominance and mating rights. These horns, which can reach lengths of up to 5 inches, are a symbol of strength and play a vital role in the beetle’s survival. The size and shape of the horns make the male beetle appear even more formidable, giving it an almost mythical appearance.
The body of the Hercules beetle is robust and covered in a hard exoskeleton that provides protection from predators. The color of the beetle typically ranges from a pale brown to a dark black, with a glossy sheen that adds to its impressive appearance. This exoskeleton, or “armor,” not only acts as a shield but also aids in the beetle’s ability to maneuver through its environment. These beetles have six legs, which are strong and equipped with sharp claws that help them climb trees and other surfaces in search of food or a mate.
The Strength of the Hercules Beetle
What truly sets the Hercules beetle apart from other insects is its sheer strength. Known to be the strongest insect relative to its size, the Hercules beetle can lift objects up to 850 times its body weight. This is equivalent to a human being able to lift a tank. The beetle’s strength is a result of its specialized exoskeleton and muscle structure, which work together to allow it to perform such remarkable feats. These capabilities are essential for survival, particularly in its natural habitat where it must compete with other males for mating rights or move large objects in search of food.
The Hercules beetle’s strength also comes into play when it uses its horns in combat. During the mating season, males engage in fierce battles with one another to establish dominance. The battles involve pushing, lifting, and flipping each other over, all using their impressive horns. The male who is able to best the other in these displays of strength is often rewarded with access to a mate.
The Lifecycle and Reproduction of the Hercules Beetle
The lifecycle of the Hercules beetle begins when the female lays her eggs in decaying wood or other organic material, which will later serve as food for the larvae once they hatch. The eggs take about two to three weeks to hatch into larvae, and these larvae are the largest stage of the beetle’s life cycle. They feed on rotting wood and other organic matter, growing rapidly as they develop into pupae. This stage can last several months to a year, depending on environmental factors.
Once the larvae have fully matured, they undergo metamorphosis to become adult beetles. The process of metamorphosis involves a significant change in body structure, as the larvae transition into their final adult form. Upon emerging from the pupal stage, the adult Hercules beetle is ready to mate. The males engage in their characteristic battles using their large horns to fight for the attention of females. These battles can be quite intense, with the strongest males prevailing.
Adult Hercules beetles typically live for about two to three months, during which they continue to feed on plant matter and engage in mating rituals. After mating, the female lays her eggs, and the cycle continues.
Habitat and Distribution of the Hercules Beetle
The Hercules beetle is found in the tropical and subtropical rainforests of Central and South America. These beetles are primarily located in countries like Colombia, Panama, Costa Rica, and parts of Venezuela. They thrive in environments with abundant vegetation and access to decaying organic material, which is crucial for both the larvae and the adults. The moist, warm climate of rainforests provides an ideal habitat for these beetles, offering shelter and food resources necessary for their survival.
In the wild, Hercules beetles are often found in the forest floor or in rotting tree stumps where they can find food and shelter. They are nocturnal creatures, so they tend to remain hidden during the day and only come out at night to feed and mate. The habitats in which they are found are rich in biodiversity, supporting a variety of species that coexist in complex ecosystems.
Ecological Importance of the Hercules Beetle
As decomposers, Hercules beetles play an important role in their ecosystems. They help break down decaying wood and plant material, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process is essential for maintaining the health of tropical forests, where the accumulation of organic matter would otherwise slow down the regeneration of the ecosystem. By feeding on rotting organic matter, Hercules beetles help prevent the buildup of dead plant material, ensuring that nutrients are returned to the soil to nourish new plant growth.
In addition to their role as decomposers, Hercules beetles are an essential food source for various predators, including birds, reptiles, and other insects. Their size and presence in the ecosystem make them an important part of the food web in tropical rainforests.
Conservation Status of the Hercules Beetle
While the Hercules beetle is not currently considered endangered, habitat loss and deforestation pose potential threats to its population. As rainforests are cleared for agriculture and urban development, the beetle’s natural habitat is shrinking, potentially impacting its ability to thrive. Conservation efforts aimed at preserving rainforests and their biodiversity are crucial to maintaining the populations of Hercules beetles and other species that depend on these ecosystems.
Efforts to raise awareness about the importance of these insects and their role in maintaining ecological balance are essential. By supporting conservation initiatives and sustainable practices, we can help ensure that the Hercules beetle continues to thrive in its natural environment.
More Read: https://trustwiki.com/https-techzoneelectronics-com-finance/
Conclusion
The Hercules beetle is a fascinating creature that embodies strength, resilience, and ecological importance. With its incredible size and remarkable strength, it has earned its place as one of the most awe-inspiring insects on the planet. From its impressive physical features to its vital role in the ecosystem, the Hercules beetle offers a glimpse into the wonders of the natural world. By understanding its lifecycle, habitat, and significance, we can better appreciate the unique role it plays in maintaining the health of tropical rainforests. As we continue to face environmental challenges, the Hercules beetle serves as a reminder of the delicate balance that exists within nature and the importance of preserving the habitats that support such incredible species.
FAQs:
What is a Hercules beetle?
The Hercules beetle (Dynastes hercules) is one of the largest and strongest beetles in the world. Known for its impressive size and strength, it is found primarily in the rainforests of Central and South America.
How strong is the Hercules beetle?
The Hercules beetle can lift objects up to 850 times its body weight, making it the strongest insect relative to its size.
Where do Hercules beetles live?
Hercules beetles are found in tropical rainforests in Central and South America, particularly in countries such as Colombia, Panama, and Costa Rica.
What do Hercules beetles eat?
Hercules beetles feed primarily on decaying wood and plant matter, which they help break down as part of their role as decomposers.
Are Hercules beetles endangered?
While not currently endangered, the Hercules beetle faces potential threats from habitat loss due to deforestation. Conservation efforts are crucial to protecting their populations.
Visit for more, Truswiki